Context of the report: summary
The main idea: the Internet market is saturated because more than half of the world’s population is already online.
- Smartphones supplies fell for the first time and the e-commerce growth rate is also slowing, although it will not reach the ceiling for a long time.
- In the upcoming years, there will be a battle for regional and local markets. Direct delivery and fintech are the leaders in 2019. Freemium has become the most sustainable and promising business model.
- Space for growth creates innovation in data collection and analysis. The more companies know about the customer, the more favorable conditions and attractive products they offer.
- Consumers increasingly value privacy, which is why their data is becoming more expensive.
- Social media is struggling with problematic content – from fake news to extremism – but not as successfully as we would like. This will be the main course of their effort.
Connected humanity
Main idea: only a few dozen Internet companies serve 4 billion people. The “blue ocean” of new users is no more.
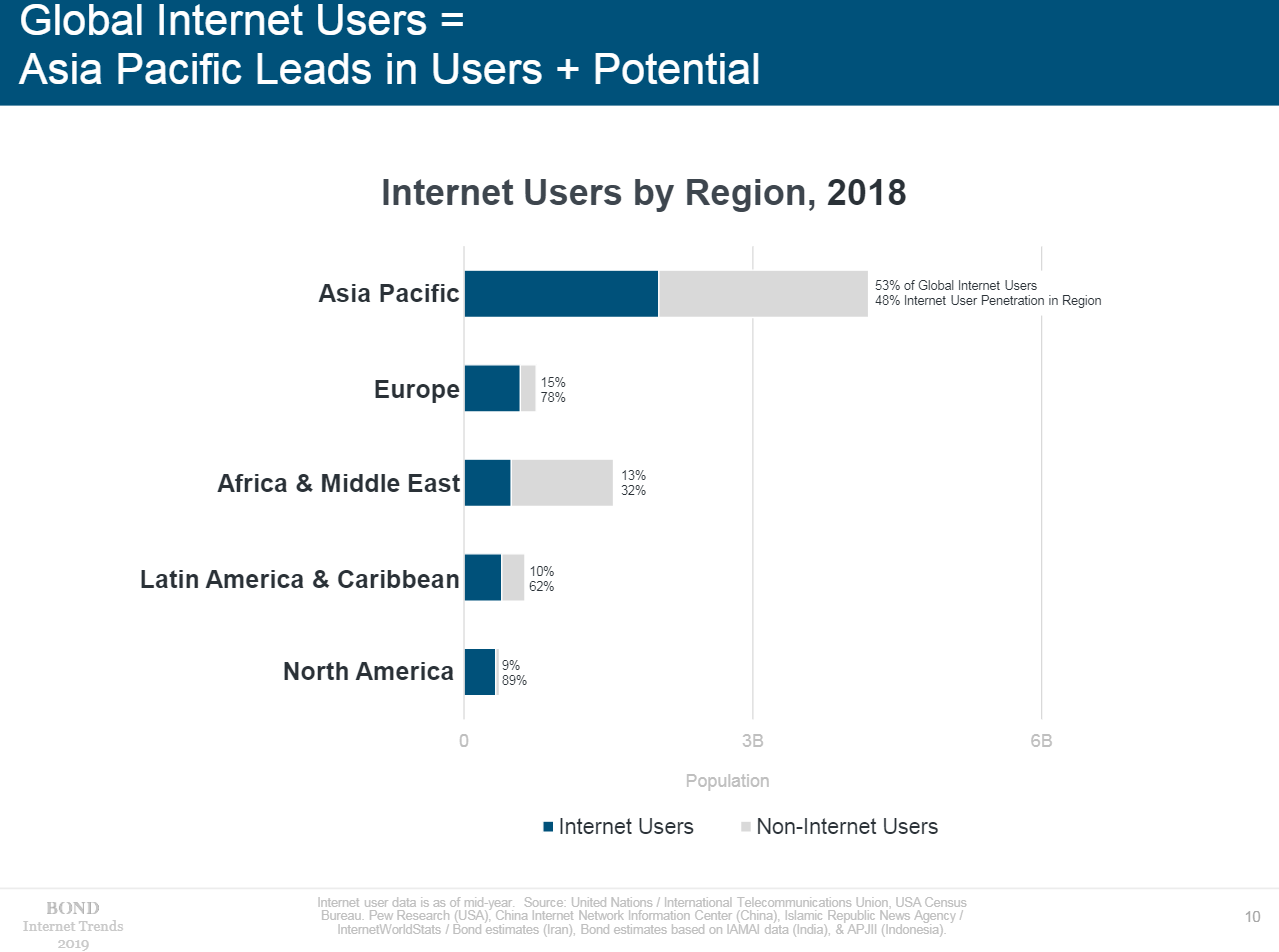
- In 2019, 3.8 billion people or 51% of the world’s population, regularly accesses the Internet. Over half of them live in the Asia-Pacific region, China, India, and the USA occupy the top three places in terms of the number of users.
- Fewer new users access the Internet and the growth rate of the audience decreases. All these billions of users are disassembled and served by technical companies.
- 9 of the 30 largest companies in the world are working in the tech sector. In three years, the cumulative capitalization of the 30 largest tech companies doubled. 25 of the 30 largest tech corporations operate in the United States (18) and China (7).
- The technology market is extremely concentrated in the hands of several huge companies, among the top 10 most expensive companies in the world, 7 are tech and only two of those are among the second dozen: Samsung and Cisco.
E-commerce and advertising
Main idea: big data overturns e-commerce and advertising industry.
- E-commerce grew by more than 12% y/y, while traditional retail grew by 1.5-2%. Online trading already took 15% of the total retail (a year ago it was 14%).
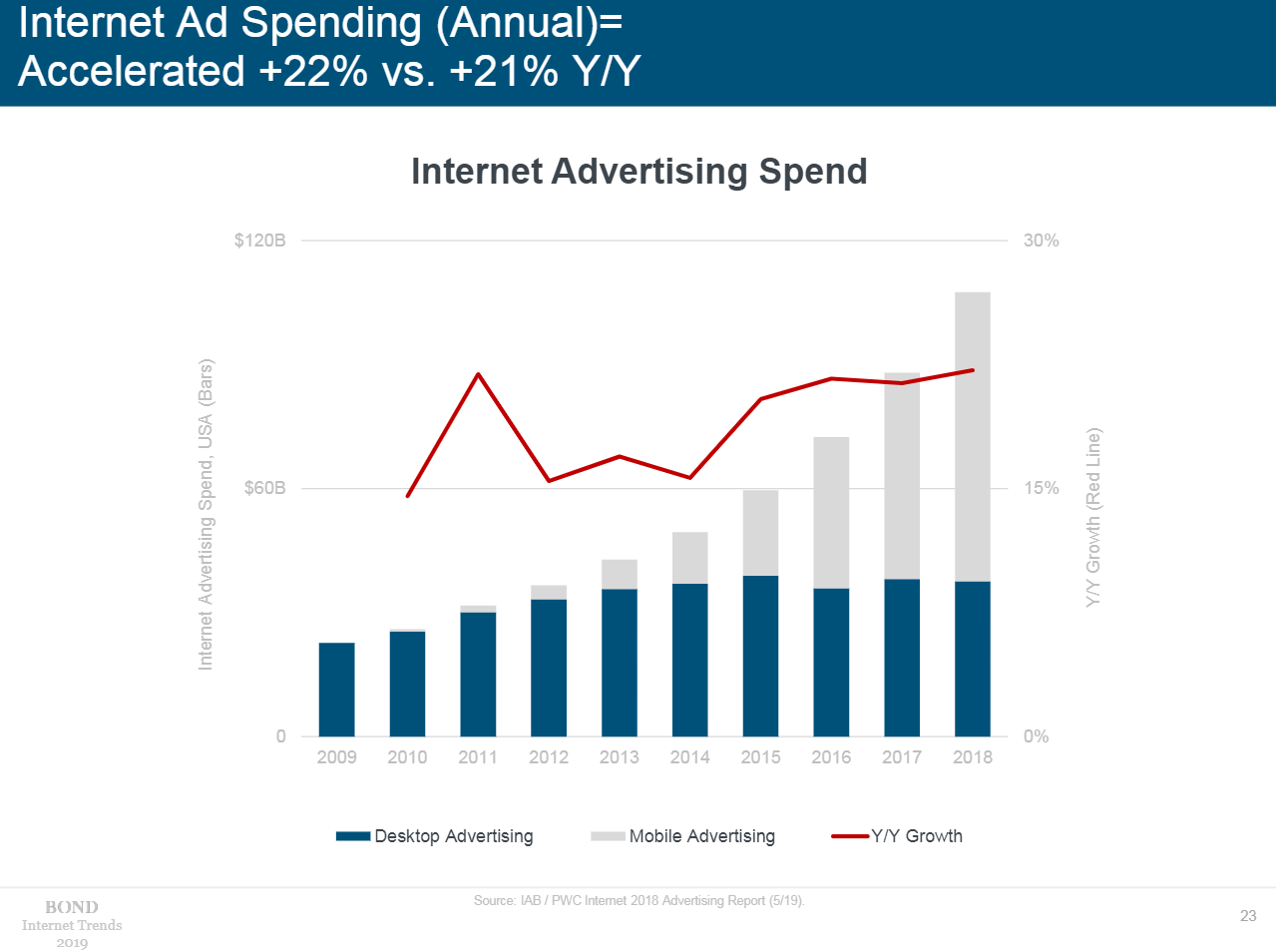
- The advertising landscape has completely changed. Less than 10 years ago, advertisers underestimated the digital environment. Now one-third of the budgets are spent on mobile ads and another 18% on desktop.
- Advertising is being placed algorithmically. It is often more profitable for advertisers to search for the audience rather than contact the platform. As a result, the vast majority of funds goes to large platforms – Google, Facebook, and several smaller ones – Amazon, Twitter, Snapchat, Pinterest. This change was made possible by machine learning and related technologies.
- Advertising in 2019 has one main problem and one opportunity. The problem is privacy, which will significantly complicate targeting. Opportunity – tracking across multiple platforms. Users are spending more time surrounded by multiple screens, thus leaving more data.
Chinese Internet miracle
The Chinese section of the presentation was prepared not by Meeker, but by Hillhouse Capital, which specializes in the Asian market, but it is one of the most exciting pieces.
Main idea: China’s 817 million mobile Internet users is a model of development for many markets.
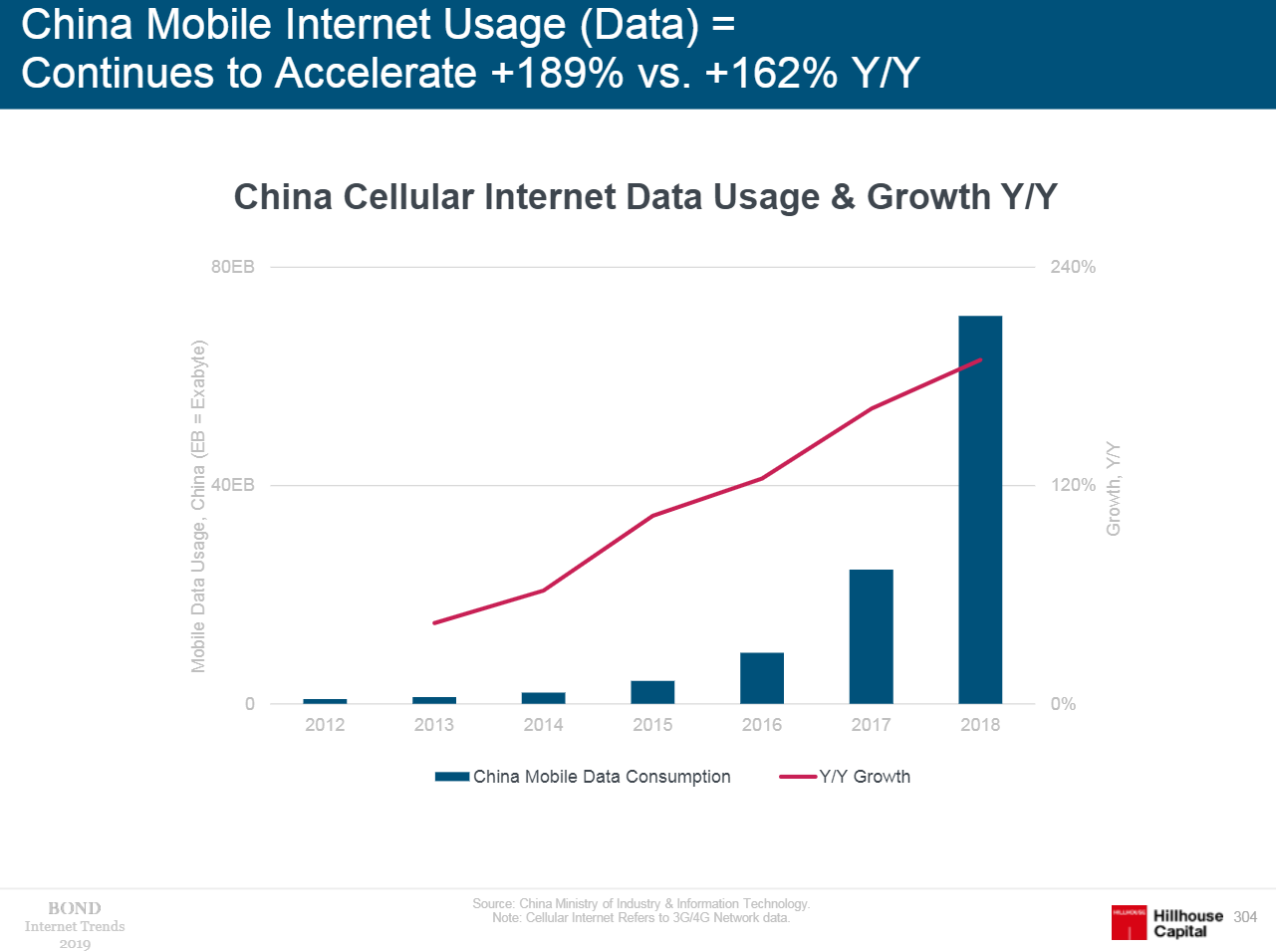
- The main content consumed by the Chinese is short videos, daily users from China watch 600 million hours of short videos. This is the main reason why the growth of mobile traffic almost tripled in 2018.
- Games accompany visual content. WeChat messenger mini-games transformed payments, e-commerce, retail, and education sectors. Useful mini-apps attract tens of millions of users.
- The Chinese tend to use super applications (super-apps). For example, Meituan, initially an application for joint purchases, now unites over 30 services, and the number of its users in 2018 increased by 26% and reached 412 million. The Alipay payment service now combines 200,000 mini-applications, a billion users, 70% of whom use 3 or more financial services.
- The strategy of super applications has been adopted in other countries around the world.
- Video streaming is the foundation of e-commerce. Streaming and influencers make the choice transparent, interactive, and fascinating. This is an excellent solution for the digital generation. In the meantime, offline stores are digitizing themselves, linking consumers, products, and virtual sites.
How the Internet is used
The main idea: the Internet is a universal means of communication with everything that man has created and the business has to offer. People will spend more time with devices and will find more ways to use them.
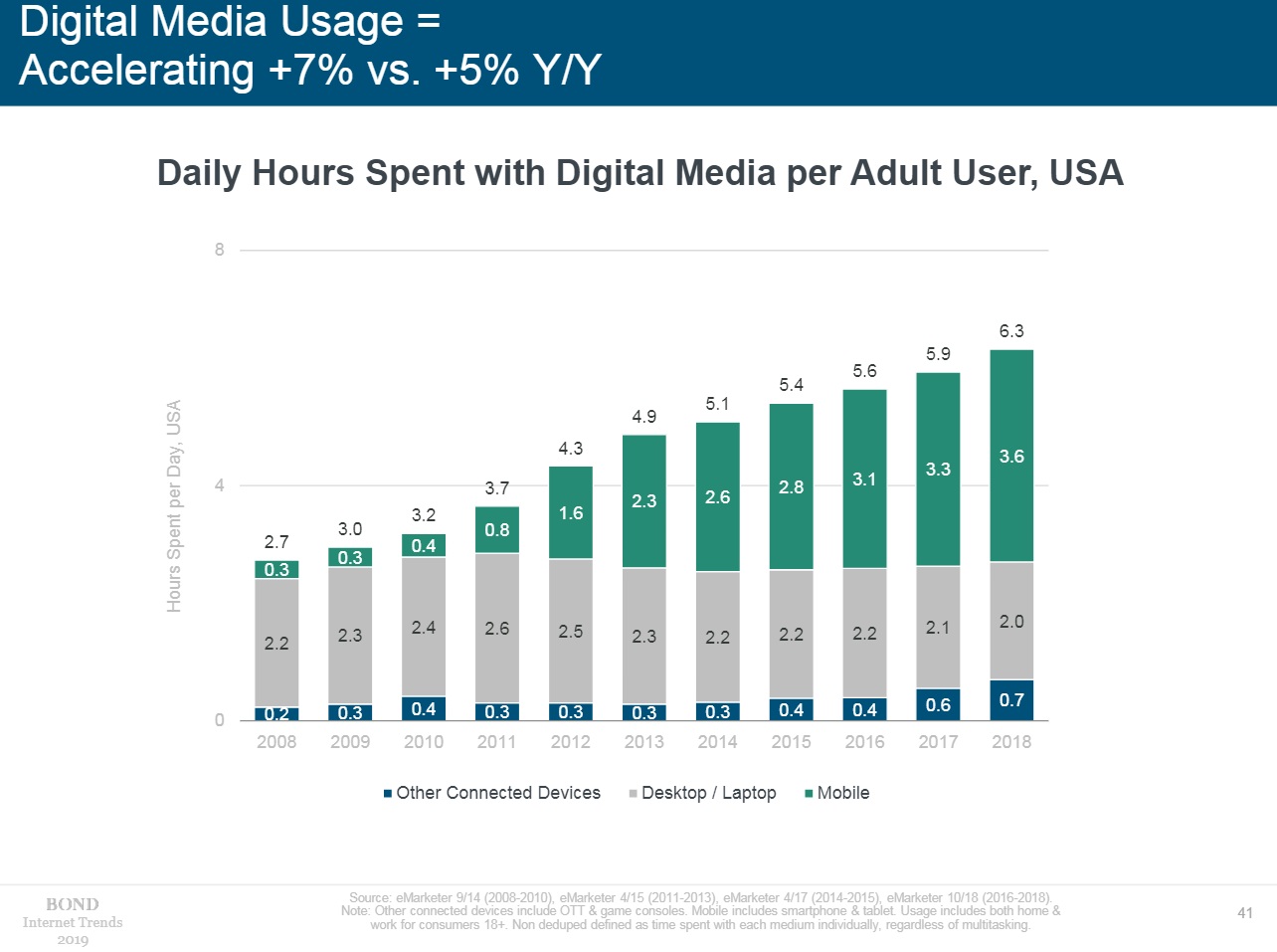
- Users are dedicating more and more time to digital media. This figure rose by 5% in 2017 and 7% in 2018, the fastest growth since 2012. An adult American spends 6.3 hours a day with digital devices, including 3.6 with a mobile device. For the first time, the mobile screen is watched more than TV (226 minutes versus 216).
- Visual formats, including “stories,” show incredible growth. Instagram and YouTube show the most actively growing consumption. In the US, watching digital video takes 28% of the total viewing time (the rest is on TV).
- Podcasts – another non-textual genre – are no longer a niche format. Over the past four years the audience has doubled and reached 70 million people in the United States.
- Wearable devices show stable growth. In 2014, there were 25 million users, in 2018 – 52 million.
- The voice-activated devices market is growing much faster. Amazon Echo speakers are installed in 47 million houses, a figure that doubled in a year.
- Delivery, transport, financial services, online marketplaces, etc. – their target audience shows the fastest growth, from 25 to 56 million over two years in the United States. The report lists dozens of examples of rapid growth in various fields – from the Indian mobile ecosystem Reliance Jio to the European Revolut, which doubled the number of personal banking customers in 10 months.
- Instead of text, people switch to images/videos and related technologies. Even on the originally text-oriented Twitter, over 50% of views belong to images, videos, and other types of media. Mary Meeker is confident that the evolution of the visual trend will lead to severe changes in design, collaboration, and entertainment.
- Humanity is playing and having fun. The number of players and consumers of interactive entertainment in 2018 increased by 6% and reached 2.4 billion.
Internet use: concerns and good news
The main idea: while the platforms are looking for a cure to sleep deprivation and harassment on the Internet, states issue legislative acts meant to block, supervise, and repress politics. Users try to protect themselves by hiding and encrypting personal information.
- The main concern is information overload. In 2018, 28% of adults in the US were “almost constantly” online. In the group aged 18-29, the figure was 39%. 63% of adults try to limit the time spent online.
- The main positive social media feature is the opportunity to express yourself. The main negative – the quality and quantity of sleep. The largest platforms help users control the time spent in particular applications and with devices turned on. The time spent in social media is now slowing its growth, but still growing.
- People are concerned about privacy. This concern decreases slightly over time, but regulators come up with new laws and platforms have to implement new solutions to ensure privacy. The demand for information encryption and instant messengers with end-to-end encryption is growing. In three years, the share of encrypted traffic increased from 53% to 87%.
- Serious issue – questionable content. The whole spectrum – fake news, abuse, negative news background, extremism, propaganda, and bullying. All of this is transformed from text to audiovisual, enhanced by recommendation algorithms and encouraged by social media. Platforms – Facebook and YouTube – are fiercely trying to reduce the volume of such content and hire thousands of moderators.
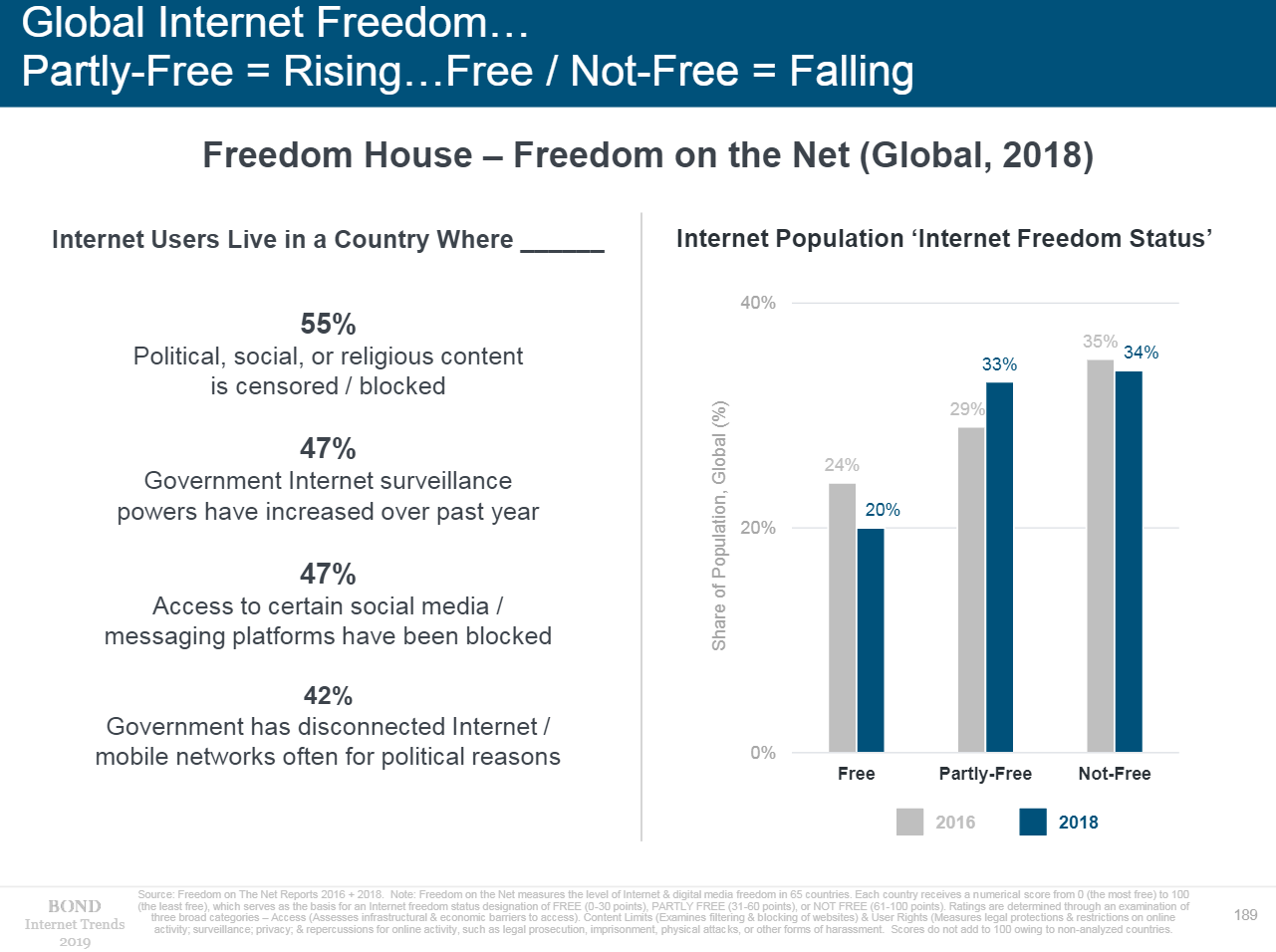
- Internet is not free. 55% of users live in countries with content partially blocked, and 47% – with government supervising the network. The same percentage has faced social media and instant messengers blocking. For 42% of Internet users, their government regularly cuts Internet and mobile networks for political reasons.
- The global Internet is divided into countries’ sub-nets, each of them has its regulation, even though everyone would benefit from the open Internet.
- Cyber attacks and warfare will continue and intensify, including attacks sponsored by states.
Freemium – the business model of the future
The main idea: not only videogames market benefit from selling the improved user experience.
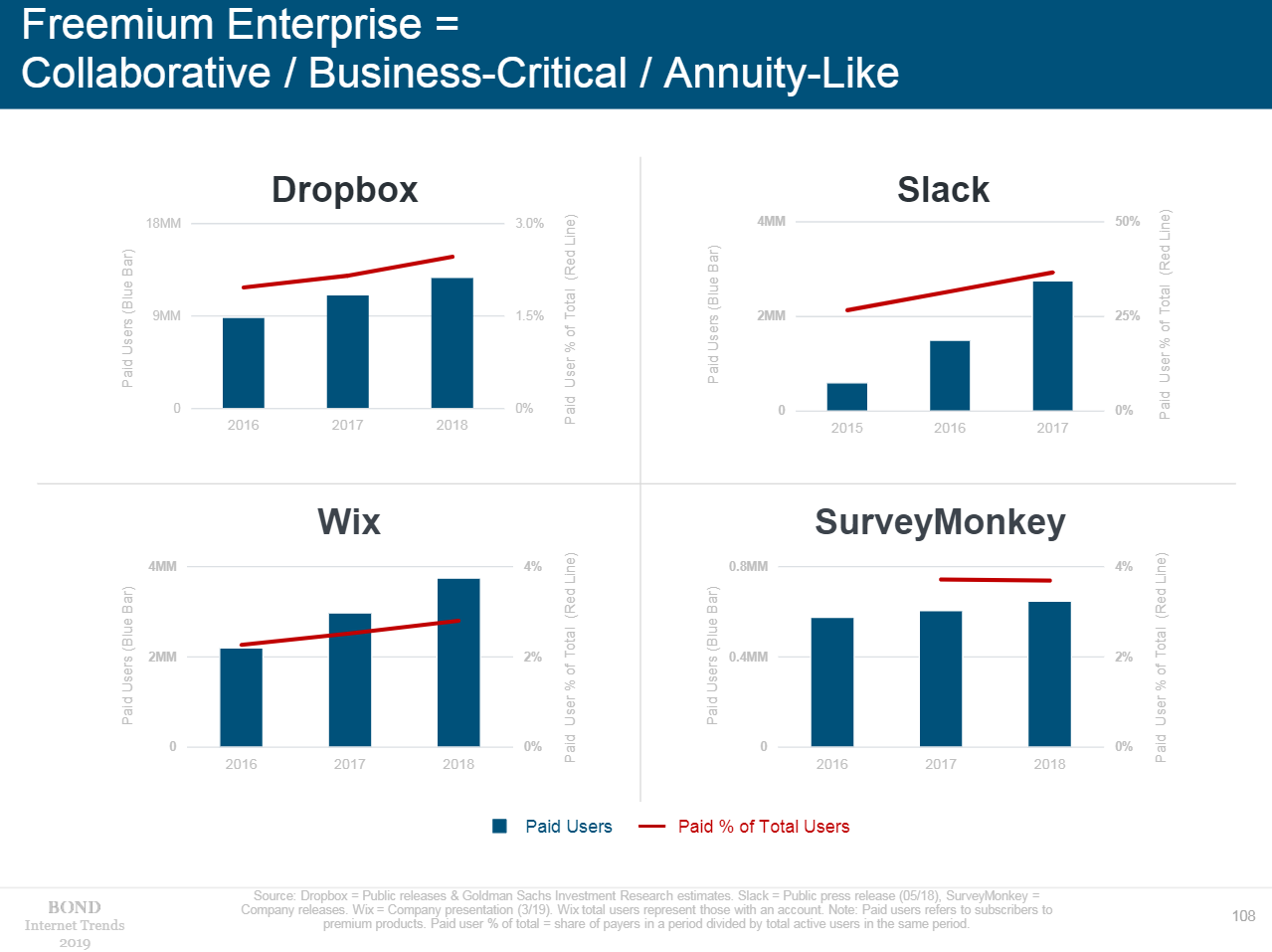
- End users are willing to pay for a reliable product after they try it — the essence of the freemium model – a free trial or basic service and a paid improved one. In 2018, over 40% of Spotify users paid for good playlists. More or less the same for Amazon Prime.
- Freemium has been tested for more than ten years in three sectors – videogames, service for corporations, and applications for end users. This route is not even close to an end. One of the leaders is Google, as it offers its application package for free and increases the number of paid users.
- The main goal of this business model is to increase paid users’ share, preferably have a significant one from the beginning. Depending on the product, the figure may be less than 1% (games created Rovio) and more than 25% (corporate messenger Slack).
- Two key freemium drivers are: first – cloud services that simplify the deployment of web applications; second – effective digital payments.

Data Growth – Revolutionary Change
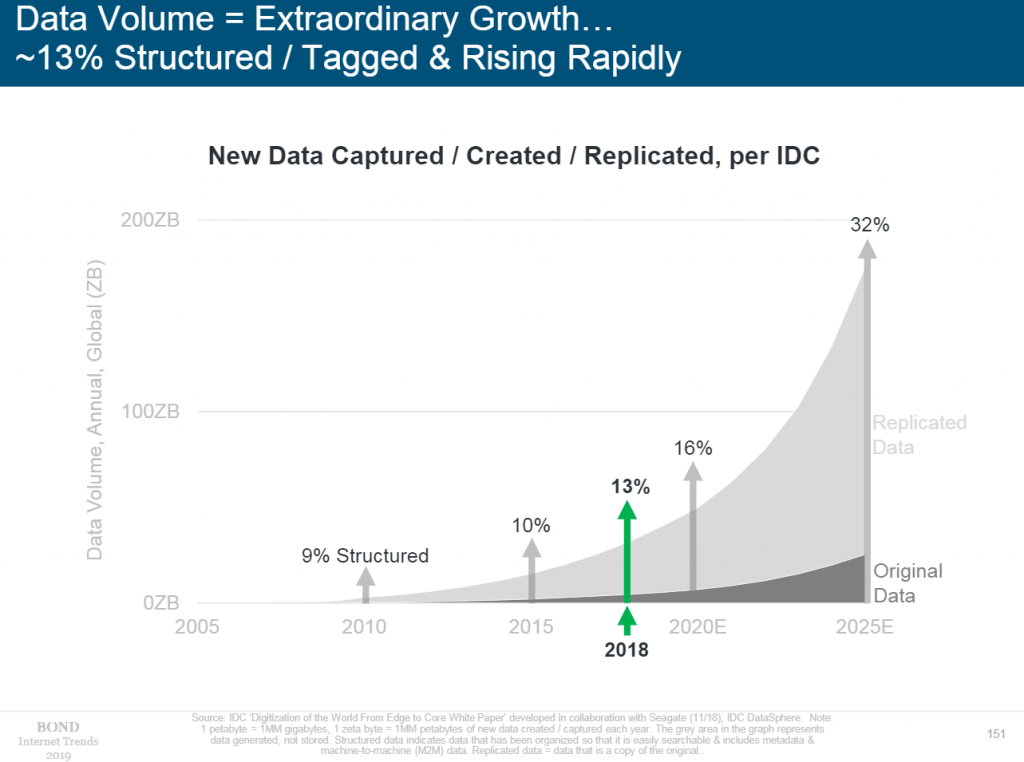
The main idea: humanity does not have time to process the collected data.
- While before applications consisted of code and data, now data itself has become a new application. Applying artificial intelligence techniques to big data can improve user experience.
- The rate at which the volume of data collected, created, and copied is growing is accelerating every year. In 2019, the amount of cloud data will exceed the amount of data stored by the user. By 2022, clouds will bypass data stored on corporate servers.
- The ability of a person to adapt to changes is already behind the speed of technological changes. This ability can be adjusted and improved through new educational mechanisms.

Online education
The main idea: the demand for knowledge is higher than ever and will grow further.
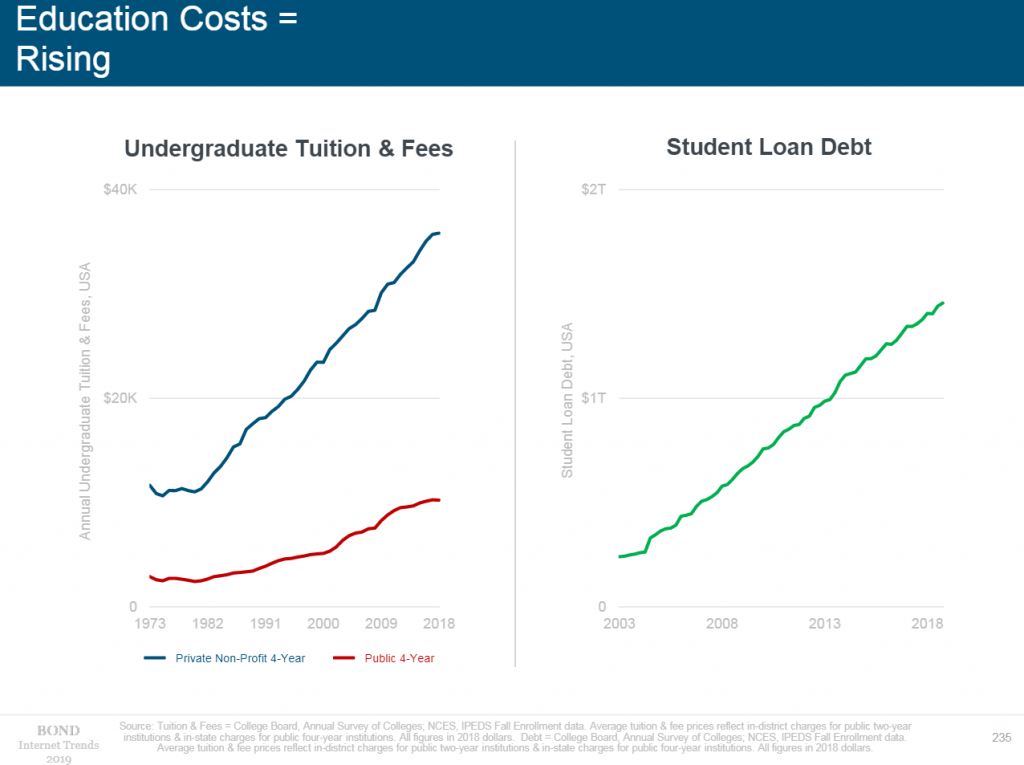
- Offline education cost is growing; students are increasingly turning to online platforms. The share of offline students in 2012 was 74%. In 2017, it fell to 67%. Many universities have already released their online programs and offered to complete a master’s degree in a variety of areas (including MBA).
- All online platforms and marketplaces are seeing a sharp increase in students and teachers.
- New business models are emerging: payment at the expense of a portion of income after employment (Lambda School), a subscription for educational assistance (Chegg), a self-study constructor (Quizlet). Separate huge demand arises for additional school education and teacher-school-parent communication. This is especially evident in emerging markets in the field of language learning.
- 59% of users from generation Z call YouTube their preferred learning tool. 4.5 billion hours of video instructions are watched on YouTube every year.
- In online education, there is still a strong bias in the technology side. 80% of Coursera’s revenue comes from technology, data analysis, and business courses. The most popular courses are machine learning, learning to learn, maintaining health, and cryptocurrency.